Salivary Gland Cancer
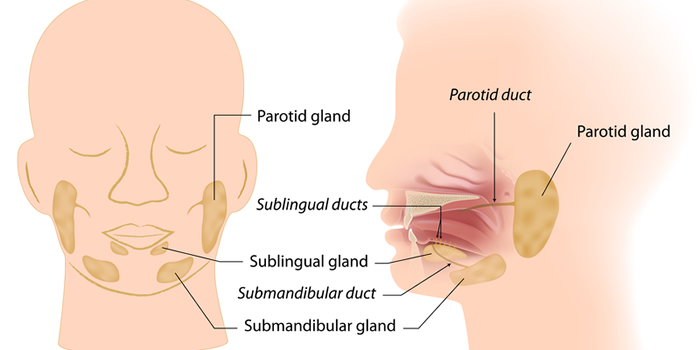
Salivary gland cancer is a tumorous growth that develops on the salivary glands. The salivary glands are underneath and behind the jaws. There are actually three pairs of salivary glands, including the parotid, sublingual, and submandibular glands. Any of these glands can produce a cancerous growth, but the condition is most common in the parotid glands, which are located close to the ears.
Symptoms of Salivary Gland Cancer
The most common symptom of salivary gland cancer is a firm lump or growth near the salivary glands. The swelling could be located near the jaws, ears, or around the neck or mouth. Other common symptoms of salivary gland cancer include numbness in part of the face, muscle weakness on one side of the face, and persistent pain on one of the salivary glands. You might also notice difficulty swallowing and trouble opening your mouth widely, such as when you need to yawn. Many non-cancerous salivary gland disorders have similar symptoms as cancer, which is why it is important to contact a physician if you develop any of these symptoms. An ear, nose and throat doctor or otolaryngologist can make the diagnosis between a cancerous condition and a non-cancerous growth with the help of the examination, imaging, and a needle biopsy.
Risk Factors for Salivary Gland Cancer
There are several risk factors that can increase your chances of getting salivary cancer. If you have had radiation treatments to your head or neck for a previous cancer, then you have an increased risk of salivary gland cancer. HIV and the Epstein-Barr virus infections also increase the risk of salivary gland tumors. Occupational exposures to asbestos, lead, rubber manufacturing materials, and plastics manufacturing materials can also increase your risk of this cancer. Salivary gland cancer is more common with increasing age.
Treatments for Salivary Gland Cancer
There are different types of salivary gland cancers, some of which are more aggressive than others. Your physician will do a biopsy to determine which type of salivary gland cancer you have and then formulate a specific treatment plan based upon the stage and type of your cancer.
The most common treatment used by an otolaryngologist for salivary gland cancer is surgery. The physician may remove the tumor or the entire salivary gland. If the cancer has spread to nearby salivary glands, those may also be removed. If the cancer has spread into the lymph nodes of your neck, the physician may need to remove those as well. In some cases, you may need reconstructive surgery after the cancer has been removed. Your doctor might also order radiation therapy or chemotherapy to eliminate any remaining cancer cells.
Prognosis
When salivary gland cancer is detected and treated at an early stage, most people go on to live a normal and long life. The earlier the cancer is treated, the higher your chances of becoming a survivor. You can also take actions to lead a healthy lifestyle to improve your recovery. This includes getting enough rest while recovering from surgery or participating in chemotherapy or radiation treatments for salivary gland cancer.

